Contents
Developing a systemic approach adapted to the various local challenges is no simple matter. Existing methodologies are often complex, difficult to apply and do not always provide a complete strategic vision. To overcome these limitations, we propose to approach the "Make or Buy" issue through a simple tool that takes into account all the dimensions of the subject.
A complex Make or Buy strategy
- Accurately assess return on investment
- Precisely identify in-house skills
- Evaluate teams' production capacity
- Define key business activities
The iQo "In-Out" decision matrix
To address this issue, we have developed the "In-Out" matrix. With its four distinct categories, it enables us to analyze and clarify the positioning of each activity, distinguishing the appropriate strategies.
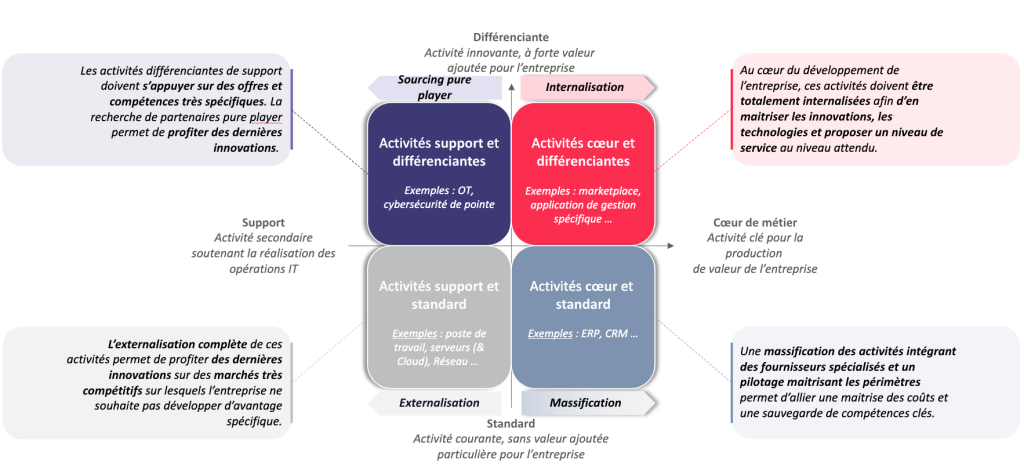
The construction of the matrix (see image above) is based on a horizontal analysis of the company's value chain, enabling differentiating activities to be identified. The vertical axis is based on the level of standardization of the activity on the market. Each dial proposes a clear strategy:
This category encompasses differentiating support activities that require highly specific offerings and skills, such as cybersecurity. On the one hand, IT Departments outsource some of these activities to "Pure Player" suppliers, taking advantage of the latest innovations, while on the other, they internalize those that give them a competitive edge in the marketplace.
These are core business activities, directly linked to strategy and innovation, such as a marketplace or a customized application. These activities must be internalized in order to control developments and technologies, and to offer a certain level of service. By doing so, the IT Department retains control over all critical activities, and moves closer to the "digital native" model.
This category covers day-to-day support activities, such as workstation and server management. Outsourcing these activities enables us to take advantage of the latest innovations from specialized suppliers in highly competitive markets. This optimizes operational efficiency and reduces costs, while focusing on high value-added activities.
Conclusion
The "In-Out" matrix provides insight into a complex and constantly evolving IT environment. It helps IT Departments to accurately assess the value of each of their activities, in order to align their "Make or Buy" strategy with corporate objectives. Thanks to this reference model, the IT Department can make clear decisions to maximize its overall performance, optimize its investments and focus its resources on high value-added activities. At the same time, it retains a degree of control over critical activities, while taking advantage of external innovations.
Beyond operational efficiency, the "In-Out" matrix transforms the organization of the IT Department, placing digital capabilities at the service of competitiveness and differentiation. The IT Department thus becomes a strategic pillar, contributing directly to the company's success and fostering continuous innovation.

Structuring a Data and AI service offering
Structuring a Data & AI service offering is a key lever for encouraging adoption and developing governance on these subjects. Indeed, without a service offering

Software Asset Management: definition and benefits
Software Asset Management (SAM) is a strategic process aimed at proactively and efficiently managing the software used by our customers.

Cloud Computing, from ownership to consumption
From ownership to "on demand" consumption? The notion of ownership, of financial assets, has long reassured entrepreneurs and shareholders. Owning your own information system, your own technological infrastructure



